Diagnóstico Costero de la Región Tijuana-San Diego

Nuestro Objetivo
El propósito de la Una Costa, Una Comunidad iniciativa apoyado por este Diagnóstico Costero de la región de San Diego, Tijuana y Rosarito,es generar y difundir información accesible sobre la calidad del agua y la erosión costera en la región de San Diego, Tijuana y Rosarito a través de un ciencia abierta y un enfoque de participación ciudadana.
Este enfoque tiene como objetivo facilitar la comprensión de la vulnerabilidad climática y promover comunidad binacional el empoderamiento para una mayor resiliencia.
Se anima a los miembros de la comunidad, educadores y autoridades locales a usar el informe elaborado por Proyecto Fronterizo de Educación Ambiental en 2023 y el tablero interactivo desarrollado por el/la Foro Permanente de Aguas Binacionales a crear su propio Mapa de Contaminación del Agua
Justificación del Diagnóstico Costero
La creciente frecuencia de eventos climáticos extremos debido al cambio climático subraya la importancia de lograr una mayor resiliencia costera.
Según la Unión Internacional para la Conservación de la Naturaleza (UICN), se invertirán 94 billones de dólares en infraestructuras de protección a nivel mundial en los próximos 20 años debido al cambio climático.
El Informe sobre la Brecha de Adaptación 2023 del Programa de las Naciones Unidas para el Medio Ambiente (PNUMA) destaca de igual manera que invertir en adaptación y mitigación —guiado por conocimientos como los de este Diagnóstico Costero— puede reducir sustancialmente los costos climáticos futuros.
Lee el Informe Completo del Diagnóstico Costero
En este contexto, la región Tijuana-San Diego enfrenta desafíos significativos debido a su vulnerabilidad climática y alto estrés hídrico. Las lluvias intensas y repentinas, combinadas con el aumento de las temperaturas, causan daños importantes a la infraestructura de la región.
Este Diagnóstico Costero subraya cómo estas presiones combinadas intensifican los riesgos tanto para el medio ambiente como para las comunidades locales.
La disminución proyectada de las lluvias para 2040, combinada con el alto estrés hídrico, amenaza la disponibilidad de agua y exacerba los problemas de erosión y contaminación.
Descarga el informe completo "Diagnóstico de Erosión Costera y Contaminación por Aguas Residuales en la Zona Costera Tijuana-San Diego", y explorar hallazgos clave para apoyar una gestión costera más inteligente y soluciones transfronterizas.
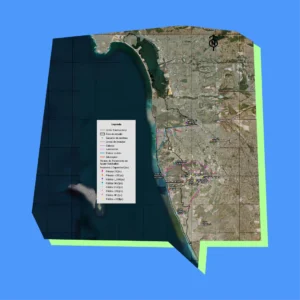
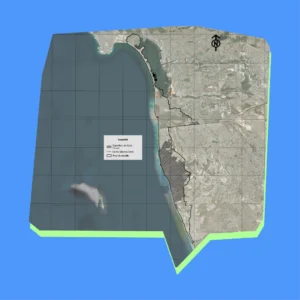
Descripción del Área de Estudio
El área de estudio abarca una superficie total de 102.4 km², de los cuales 59.3 km² se encuentran en México y 43 km² en Estados Unidos. La región costera de Estados Unidos incluye las ciudades de Coronado e Imperial Beach, conectadas por la barra arenosa de Silver Strand. En México, la zona de estudio abarca 24 km de zona costera en los municipios de Tijuana y Playas de Rosarito.

Hallazgos Clave
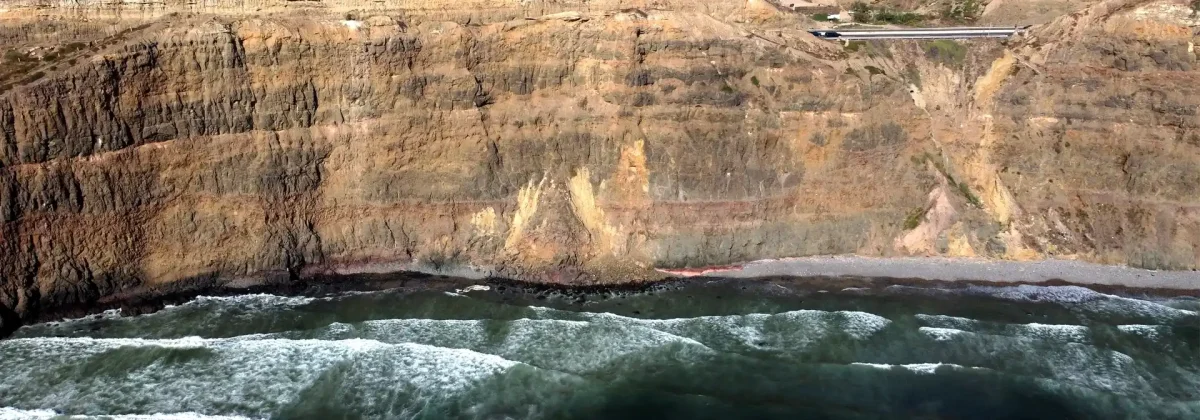
Erosión de Acantilados
La erosión de las playas y acantilados afecta tanto a la infraestructura como a los ecosistemas costeros. La geomorfología mixta de la región y la presencia de materiales sedimentarios poco consolidados agravan este problema.
Contaminación por Aguas Residuales
El vertimiento de aguas residuales sin tratamiento adecuado contamina el agua marina, afectando la salud pública y la biodiversidad. Los sistemas de saneamiento actuales son insuficientes para manejar el volumen de aguas residuales en la región.
Principales Problemas Identificados
Infraestructura de Saneamiento
La infraestructura para el tratamiento de aguas residuales en la zona costera es insuficiente. Es necesario mejorar la capacidad operativa de estas instalaciones para elevar la resiliencia de las comunidades ante condiciones adversas.
Calidad del Agua
La calidad del agua marina en la zona de estudio está comprometida por el vertimiento de aguas residuales y residuos sólidos. Los estudios de monitoreo de calidad del agua han identificado puntos críticos de contaminación que requieren atención inmediata.
Erosión y Sedimentación
La erosión costera y la sedimentación son problemas críticos que afectan la estabilidad de la infraestructura y la salud de los ecosistemas marinos. La combinación de factores naturales y antropogénicos, como el desarrollo urbano y la actividad industrial, exacerba estos problemas.
Instrumentos Institucionales
Mexico
Ha implementado políticas y estrategias para la gestión costera, incluyendo la Estrategia Ambiental para la Gestión Integrada de la Zona Costera y la creación de la Comisión Intersecretarial para el Manejo Sustentable de Mares y Costas. Sin embargo, existen limitaciones en la ejecución y financiamiento de estos programas.
Estados Unidos
Posee un avanzado sistema de gestión costera con programas como el Coastal Zone Management Act y el National Estuary Program. Además, la Asociación de Gobiernos de San Diego (SANDAG) ha desarrollado programas de monitoreo y preservación de la costa que han proporcionado datos valiosos para la planificación de proyectos de resiliencia.
Conclusiones del Informe del Diagnóstico Costero
El diagnóstico costero revela que la zona costera Tijuana-San Diego enfrenta serios desafíos relacionados con la erosión y la contaminación del agua.
Las infraestructuras actuales son insuficientes para gestionar los impactos del cambio climático, y se requiere una mayor coordinación y financiamiento para implementar estrategias de resiliencia efectivas. La colaboración binacional y la participación comunitaria son esenciales para abordar estos problemas de manera integral.
Herramientas y Datos del Diagnóstico Costero
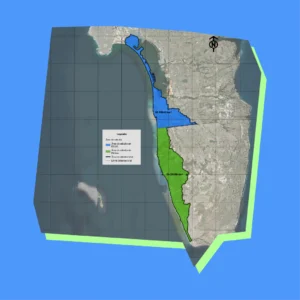
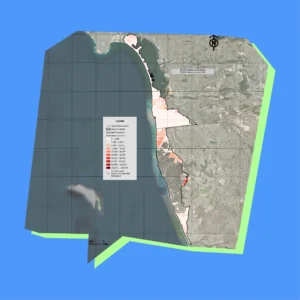
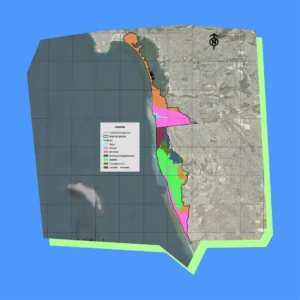
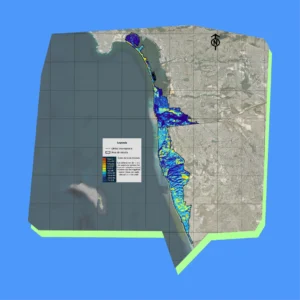
Los mapas detallados del Diagnóstico Costero revelan los riesgos de erosión, la hidrología y los patrones de uso del suelo a lo largo del corredor Tijuana-San Diego, ofreciendo archivos de alta resolución ideales para la planificación de la resiliencia costera y la protección ambiental a lo largo de la frontera entre Estados Unidos y México.
Estos mapas, creados en 2023 por Proyecto Fronterizo de Educación Ambiental, se complementan con conjuntos de datos en nuestro panel interactivo que te permiten explorar y exportar información subyacente para estrategias de gestión transfronteriza más inteligentes.